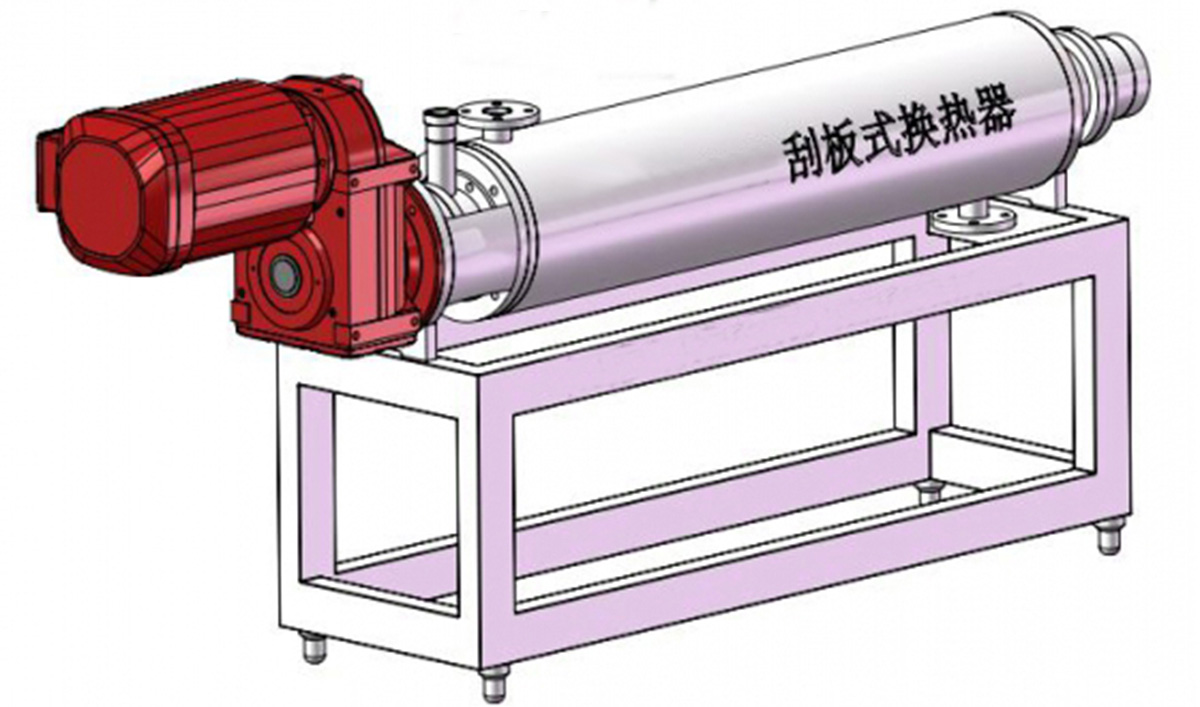
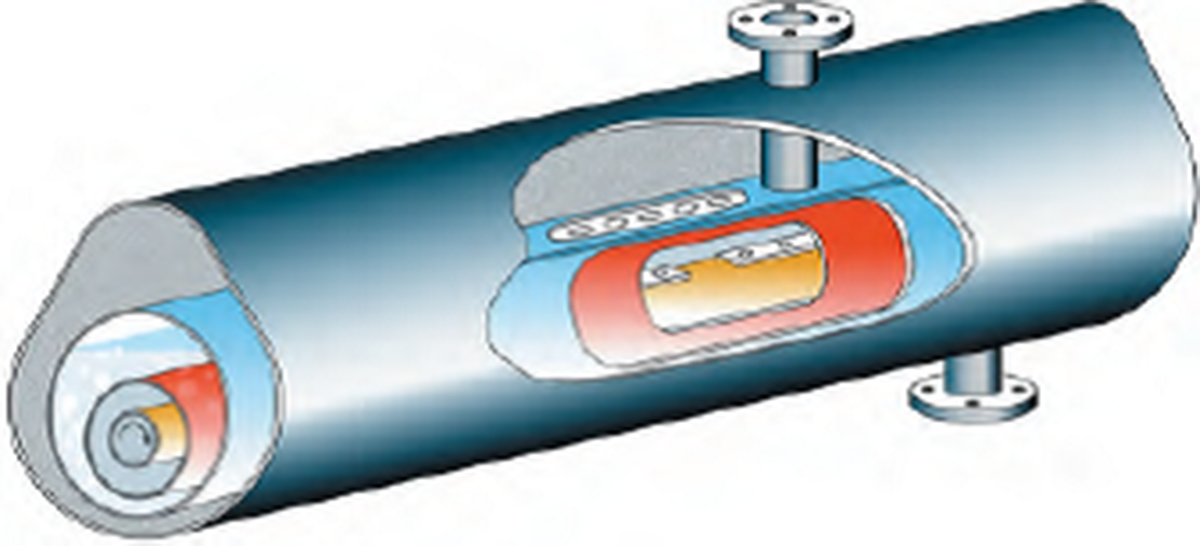
A scraped surface heat exchanger (SSHE) is a type of heat exchanger that is used to heat or cool highly viscous or sticky fluids that can't be effectively processed in traditional heat exchangers. The SSHE consists of a cylindrical shell that contains a rotating central shaft with multiple scraper blades attached to it.
The highly viscous fluid is introduced into the cylinder and the rotating scraper blades move the fluid along the inner walls of the cylinder. The fluid is heated or cooled by an external heat transfer medium that flows through the shell of the exchanger. As the fluid moves along the inner walls of the cylinder, it is continuously scraped by the blades, which prevent the formation of a fouling layer on the heat transfer surface and promote efficient heat transfer.
The scraped surface heat exchanger is commonly used in the food industry for processing products such as chocolate, cheese, shortening, honey, sauce and margarine. It is also used in other industries for processing products such as polymers, adhesives, and petrochemicals. The SSHE is favored for its ability to handle highly viscous fluids with minimal fouling, resulting in higher efficiency and longer operating times than traditional heat exchangers.
Post time: Feb-24-2023