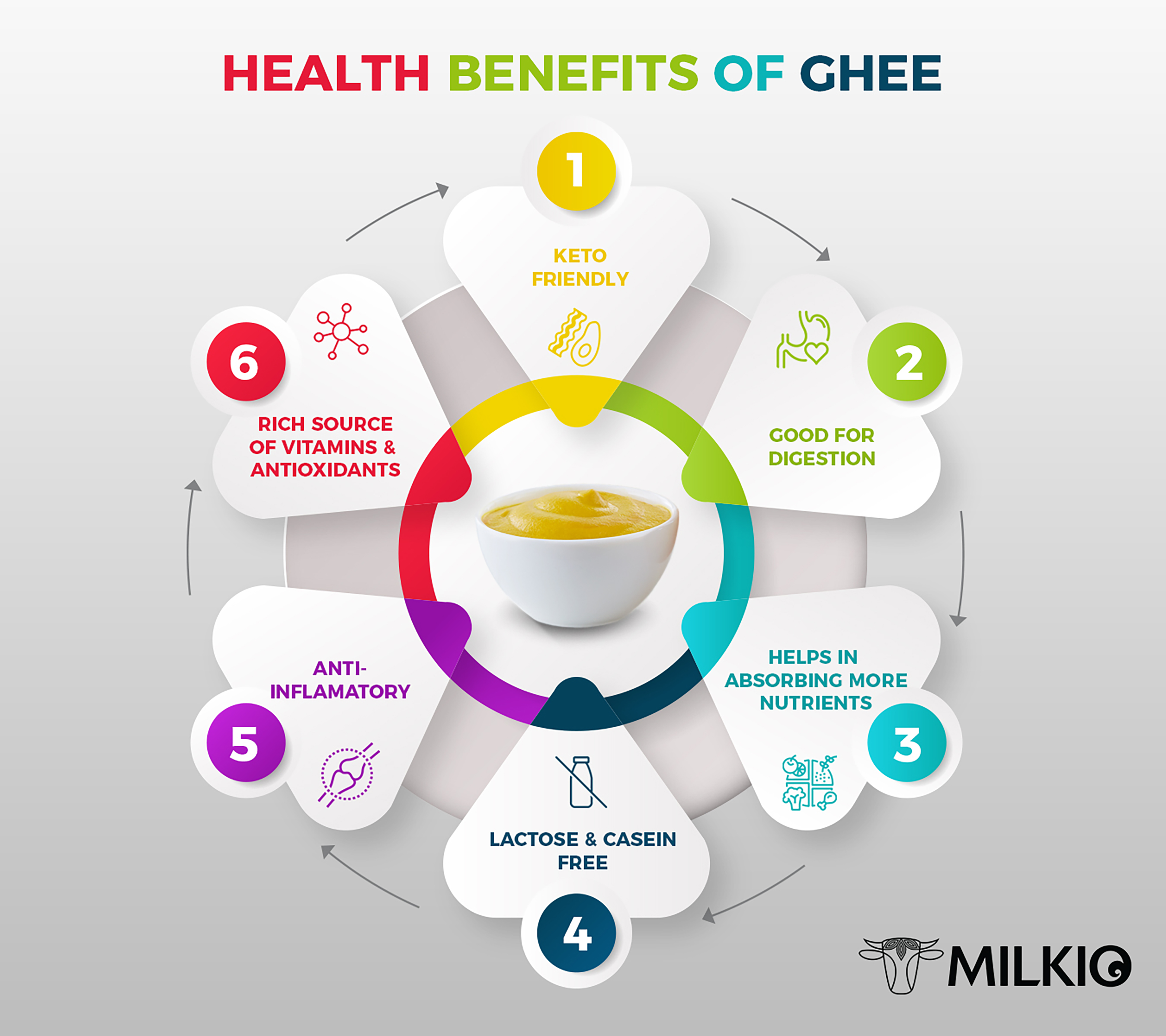
What is Vegetable Ghee?
Vegetable ghee, also known as vanaspati ghee or Dalda, is a type of hydrogenated vegetable oil that is commonly used as a substitute for traditional ghee or clarified butter. It is made by a process in which vegetable oil is hydrogenated and then further processed with additives such as emulsifiers, antioxidants, and flavoring agents to give it a similar taste and texture as ghee.
Vegetable ghee is primarily made from vegetable oils such as palm oil, soybean oil, cottonseed oil, or a blend of these oils. It is widely used in the food industry for baking, frying, and as a cooking fat. However, due to its high trans fat content, it is not considered a healthy option and is recommended to be consumed in moderation. In recent years, many countries have banned or imposed restrictions on the use of vegetable ghee due to its negative health effects.
What is differnce between Shortening and vegetable Ghee?
Shortening and ghee are two different types of fats commonly used in cooking, baking, and frying.
Shortening is a solid fat made from vegetable oils, such as soybean, cottonseed, or palm oil. It is typically hydrogenated, which means that hydrogen is added to the oil to turn it from a liquid into a solid. Shortening has a high smoke point and a neutral flavor, making it a popular choice for baking, frying, and making pie crusts.
Ghee, on the other hand, is a type of clarified butter that originated in India. It is made by simmering butter until the milk solids separate from the fat, which is then strained to remove the solids. Ghee has a high smoke point and a rich, nutty flavor, and is commonly used in Indian and Middle Eastern cooking. It also has a longer shelf life than butter because the milk solids have been removed.
In summary, the main difference between shortening and ghee is that shortening is a solid fat made from vegetable oils, while ghee is a type of clarified butter with a rich, nutty flavor. They have different culinary uses and flavor profiles, and are not interchangeable in recipes.
Processing Diagram of Vegetable Ghee
Vegetable ghee, also known as vanaspati, is a type of partially hydrogenated vegetable oil that is commonly used as a substitute for traditional ghee or clarified butter in many parts of the world. The process of making vegetable ghee involves several steps, including:
Selection of Raw Materials: The first step in the process is to select the raw materials, which typically include vegetable oils such as palm oil, cottonseed oil, or soybean oil.
Refining: The raw oil is then refined to remove any impurities and contaminants that may be present.
Hydrogenation: The refined oil is then subjected to hydrogenation, which involves adding hydrogen gas under pressure in the presence of a catalyst. This process converts the liquid oil into a semi-solid or solid form, which is then used as a base for vegetable ghee.
Deodorization: The semi-solid or solid oil is then subjected to a process called deodorization, which removes any unwanted odors or flavors that may be present.
Blending: The final step in the process is blending, which involves mixing the partially hydrogenated oil with other ingredients such as antioxidants and vitamins.
After the blending process is complete, the vegetable ghee is packaged and ready for use. It is important to note that vegetable ghee is not as healthy as traditional ghee, as it contains trans fats, which can be harmful to your health when consumed in large quantities. As such, it should be consumed in moderation as part of a balanced diet.
Post time: Apr-14-2023